What is alopecia areata? Understanding This Hair Condition
As a reader, you have probably wondered at some point what alopecia areata really is. This hair condition that causes sudden hair loss can be confusing and distressing. In this article, you will get all the necessary information to fully understand what alopecia areata is, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. From the HERO Institute team, we want you to feel supported and accompanied in this process. That's why we invite you to schedule an in-person or virtual consultation with our experts to receive personalized advice and start an effective action plan.
What is Alopecia Areata?
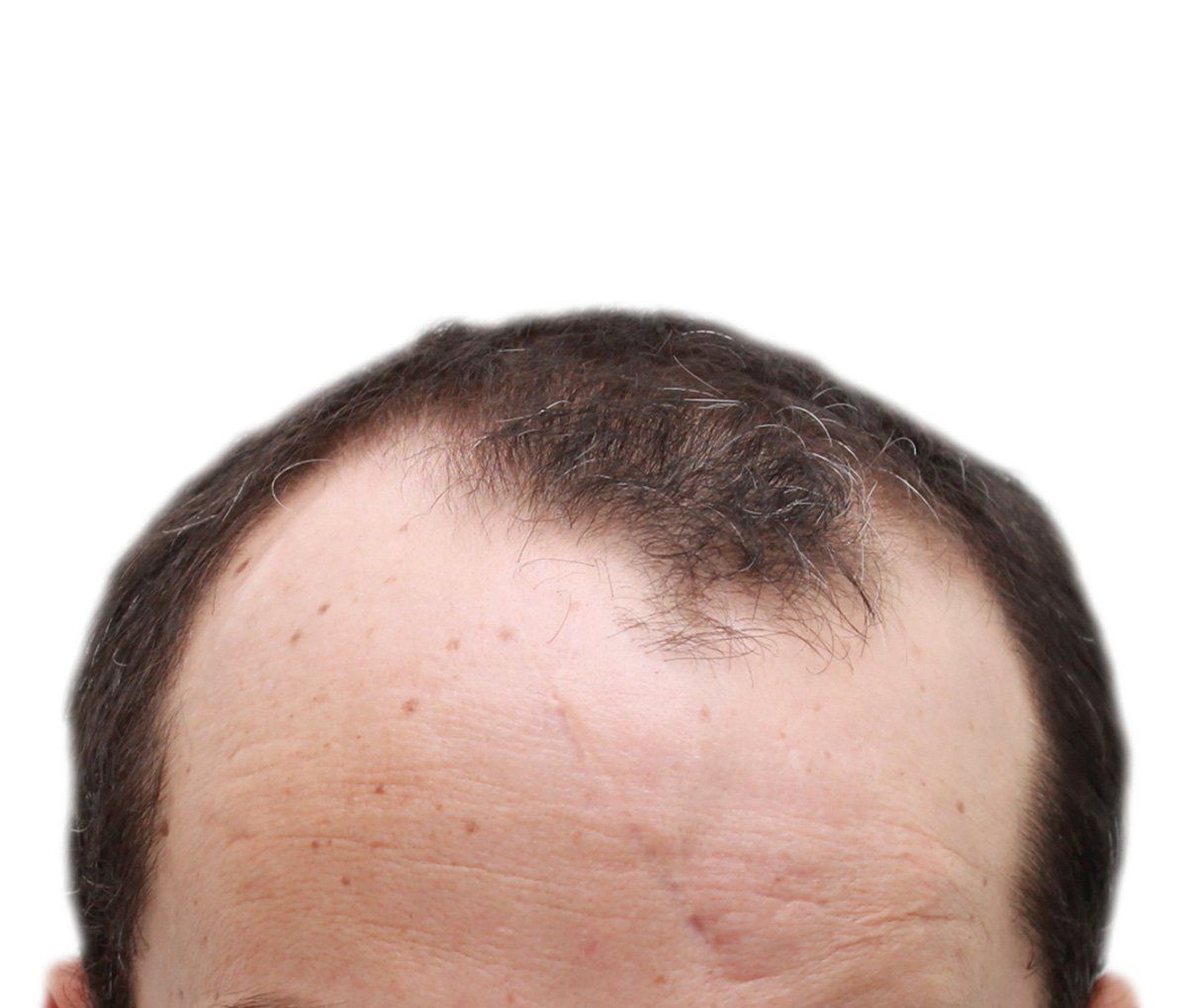
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that causes hair loss in patches, typically on the scalp. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, which are responsible for hair growth. This leads to temporary hair loss in the affected areas.
Types of Alopecia Areata
There are different types of alopecia areata based on the extent of the affected area:
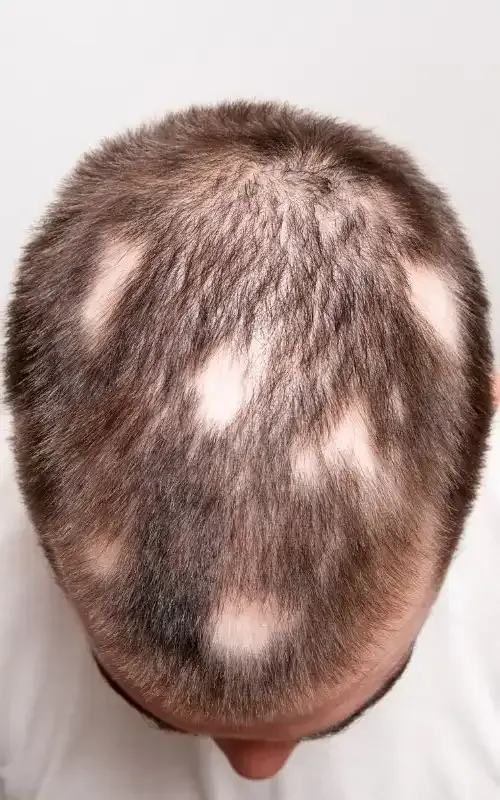
- Localized alopecia areata: Hair loss in small patches, usually less than 3 centimeters in diameter. This is the most common form.
- Totalis alopecia areata: Total hair loss on the scalp.
- Universalis alopecia areata: Total loss of hair all over the body, including eyebrows and eyelashes.
Alopecia areata is not contagious and is not a result of an infection. It is also not related to common baldness. Although the exact cause is unknown, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors that predispose certain individuals. Currently, there is no definitive cure for alopecia areata, but there are several treatments that can stimulate hair growth and control progression.
At the HERO Institute, we have a team of dermatologists specialized in alopecia areata and hair disorders. We offer precise diagnosis, personalized treatments, and follow-up to achieve the best results in hair recovery. Do not hesitate to contact us!
Causes And Risk Factors Of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. The exact reasons why this happens are not fully understood. However, some risk factors related to the development of this condition have been identified:
Genetic factors
Alopecia areata appears to have a genetic component, as it is more common in individuals with close relatives who also suffer from it. Twin studies indicate that genes contribute to approximately 55% of the risk of developing this condition.
Autoimmune issues
Individuals with alopecia areata are more likely to have other autoimmune disorders such as vitiligo, hypothyroidism, and systemic lupus erythematosus. This suggests that an imbalance in the immune system could contribute to the development of the disease.
Emotional stress
Intense or prolonged emotional stress can be a potential trigger for alopecia areata in individuals genetically predisposed. Some studies have found an association between stressful life events and the onset of symptoms. However, stress alone does not cause the disease.
In summary, alopecia areata appears to be the result of a combination of genetic, immunological, and environmental factors. Better understanding these risk factors can aid in the development of improved treatments to prevent and control this hair disorder.
Symptoms and Effects of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia Areata produces evident symptoms on the scalp and other areas of the body with hair. People who suffer from this condition experience sudden hair loss in round or oval patches. These bald areas are smooth and without scars.
Hair Loss
The main characteristic of Alopecia Areata is the loss of hair in patches. However, hair loss can also occur in other areas of the body such as eyebrows, eyelashes, and even in the beard. The speed and severity with which the bald patches appear vary in each person. Some patients may lose all their hair (alopecia totalis) or even all body hair (alopecia universalis).
Itching and Burning
Before the bald patches appear, some people report feeling itching, burning, or irritation on the scalp. These sensations can occur weeks or months before noticing the hair loss. However, not all people with alopecia areata experience itching or discomfort prior to the appearance of the bald patches.
Side Effects
In addition to hair loss, alopecia areata can cause side effects such as anxiety, stress, depression, and insecurity due to changes in appearance. It is normal for people to feel frustrated when losing their hair. However, alopecia areata does not cause any other physical symptoms nor does it pose a risk to overall health. With proper treatment, in most cases, it is possible to stop the progression and stimulate hair regrowth.
Treatments for Alopecia Areata: Minoxidil, Finasteride, Reduce Stress
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is a topical medication, available over the counter, that is applied directly to the scalp to stimulate hair growth and reduce hair loss. Originally used as a treatment for hypertension, researchers discovered that one of its side effects was hair growth. Minoxidil comes in liquid solution and foam, and should be applied twice a day. It may take 3 to 6 months of continuous use to see improvements in hair growth.
Finasteride
Finasteride is a prescription oral medication that blocks the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a male hormone that contributes to androgenic hair loss. Finasteride reduces DHT levels in the scalp and stimulates the growth of new hair follicles and hair. It may take 6 to 12 months of daily finasteride use to notice visible growth of new hair.
Reduce Stress
Chronic stress can worsen hair loss or delay improvement with other treatments. Practicing stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, regular exercise, and therapy can help alleviate stress symptoms and create a healthier internal environment for hair growth. Reducing stress will not make hair grow on its own, but it complements other treatments by improving blood circulation and oxygenation of hair follicles.
Frequently Asked Questions About Alopecia Areata: Understanding This Hair Condition
What is alopecia areata?
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune medical condition, meaning your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles. This can cause hair loss in round or oval patches on the scalp or other hair-bearing areas of the body. Alopecia areata is a common disease that affects approximately 2% of the population. Although it can be distressing, it is not contagious and rarely causes serious health problems.
What are the symptoms of alopecia areata?
The most common symptoms of alopecia areata include:
- Patchy hair loss, especially on the scalp, beard, and eyebrows.
- Patches of hairless skin visible on the scalp, beard, eyebrows, eyelashes, or body hair.
- Changes in hair texture, such as hair that feels thinner or coarser.
What are the causes of alopecia areata?
Alopecia areata occurs when the immune system attacks the hair follicles, causing hair loss. The exact causes of why this occurs are unclear, but it may be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as:
- Family history of alopecia areata or other autoimmune diseases.
- Emotional or traumatic stress.
- Other autoimmune conditions, such as vitiligo.
Alopecia areata is not contagious and is not transmitted from person to person. There is no known cure, but there are several treatments that can help manage it and, in some cases, stimulate hair growth.
Conclusion
Although alopecia areata can be a challenging disease to treat, there are various treatments available that can help stimulate hair growth and improve the appearance of the scalp. By visiting a specialized clinic like the HERO Institute, you can access personalized treatments administered by expert dermatologists. Whether you prefer an in-person or virtual consultation, our team is ready to listen to your concerns and design an effective treatment plan. Do not lose hope, alopecia areata is treatable. With the right treatment, you can see significant improvements. Let us help you on your journey towards a healthier head of hair.

We can help!
If you’re experiencing hair loss and looking for a hair restoration solution that’s right for you—congratulations! You’ve come to the right place. HERO Hair Institute is the best hair restoration clinic in Colombia, providing proven permanent hair transplant techniques and non-surgical hair loss solutions.
With over 20 years of experience, HERO Hair Institute offers you the best quality procedures in a safe, relaxed and comfortable environment. Thousands of men and women have come to HERO Hair Institute for the answers to their hair loss and hair restoration questions.